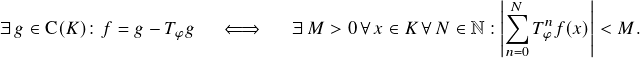Birkhoff’s ergodic theorem is arguably one of the most important theorems in ergodic theory. While being a neat convergence result, it gives very little information about how the Birkhoff averages of a function converge. Do they converge fast or slow? Is the convergence uniform, at least for nice functions? And do the averages overestimate or underestimate the limit? It is this last question that Atkinson’s Lemma addresses. These are some notes about it based on a talk by Barak Weiss. The lemma comes in several forms and below we will state one that will be useful to understand why Atkinson’s Lemma holds. To state it, denote for a measure-preserving system ![]() and a function
and a function ![]() the Birkhoff sums by
the Birkhoff sums by ![]() and the Birkhoff averages by
and the Birkhoff averages by ![]() .
.
Lemma. Let ![]() be an ergodic measure-preserving system and
be an ergodic measure-preserving system and ![]() real-valued. Then for almost every
real-valued. Then for almost every ![]() , there are strictly increasing sequences
, there are strictly increasing sequences ![]() and
and ![]() such that for all
such that for all ![]()
(1) ![]()
Assume that, eventually, ![]() for almost every
for almost every ![]() . Then Atkinson’s Lemma shows that
. Then Atkinson’s Lemma shows that ![]() and hence, by Birkhoff’s ergodic theorem,
and hence, by Birkhoff’s ergodic theorem, ![]() . In other words: If the Birkhoff sums
. In other words: If the Birkhoff sums ![]() are eventually strictly positive, then they already have to grow linearly. This phenomenon of turning a qualitative property into a quantitative one makes Atkinson’s lemma an important result for several applications, including the positivity of the top Lyapunov exponent for random walks which turns (via logarithmic reduction to the additive case) unbounded growth of random matrix products into exponential growth.
are eventually strictly positive, then they already have to grow linearly. This phenomenon of turning a qualitative property into a quantitative one makes Atkinson’s lemma an important result for several applications, including the positivity of the top Lyapunov exponent for random walks which turns (via logarithmic reduction to the additive case) unbounded growth of random matrix products into exponential growth.
Also, note that while for generic ![]() , the inequalities in Atkinson’s lemma can even be assumed to be strict, the function
, the inequalities in Atkinson’s lemma can even be assumed to be strict, the function ![]() shows that, in general, one cannot expect the inequalities to be strict for every function.
shows that, in general, one cannot expect the inequalities to be strict for every function.
Corollary. Let ![]() be an ergodic measure-preserving system and
be an ergodic measure-preserving system and ![]() real-valued. Then the following assertions are equivalent.
real-valued. Then the following assertions are equivalent.
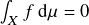
- For almost every
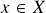 , there are strictly increasing sequences
, there are strictly increasing sequences 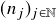 and
and 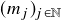 such that for all
such that for all 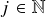
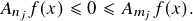
Proof. One implication follows from Atkinson’s lemma and the other implication from Birkhoff’s ergodic theorem. ![]()
Now, why should Atkinson’s lemma be true? To understand this, recall that a contraction ![]() on a Banach space
on a Banach space ![]() is mean ergodic if and only if
is mean ergodic if and only if
![]()
In light of von Neumann’s mean ergodic theorem, this means that for an ergodic measure-preserving system ![]() and a function
and a function ![]() ,
, ![]() admits a unique decomposition as
admits a unique decomposition as
![]()
where ![]() . Assume for a moment that
. Assume for a moment that ![]() lies in fact in
lies in fact in ![]() , i.e.,
, i.e., ![]() for some
for some ![]() . Then
. Then
![]()
and in this case Atkinson’s lemma follows very quickly from Poincaré’s recurrence theorem since
![]()
which is either constant if ![]() is constant or (by ergodicity) oscillating if
is constant or (by ergodicity) oscillating if ![]() is nonconstant. Most of the work in Atkinson’s lemma thus goes into extending this idea to the general case involving
is nonconstant. Most of the work in Atkinson’s lemma thus goes into extending this idea to the general case involving ![]() instead of
instead of ![]() . It is not immediately obvious why this transition should be possible since, generally,
. It is not immediately obvious why this transition should be possible since, generally, ![]() -perturbations usually do not interact well with almost everywhere convergence. Therefore, before we prove Atkinson’s lemma, it is necessary to gain a better understanding of when a function
-perturbations usually do not interact well with almost everywhere convergence. Therefore, before we prove Atkinson’s lemma, it is necessary to gain a better understanding of when a function ![]() in
in ![]() actually lies in
actually lies in ![]() and how functions in
and how functions in ![]() behave.
behave.
To understand this problem, note that
(2) ![]()
or, equivalently,
![]()
Now, if we knew that ![]() converged, than
converged, than ![]() would lie in
would lie in ![]() . However, this is almost never the case. That being said, it is not actually necessary to take a limit — it suffices to eliminate the dependence on
. However, this is almost never the case. That being said, it is not actually necessary to take a limit — it suffices to eliminate the dependence on ![]() , e.g. by taking the infimum or supremum over
, e.g. by taking the infimum or supremum over ![]() . This leads to the following criterion.
. This leads to the following criterion.
Lemma. Let ![]() be an ergodic measure-preserving system and
be an ergodic measure-preserving system and ![]() real-valued. Define almost everywhere
real-valued. Define almost everywhere
![]()
Then ![]() . If
. If ![]() , then
, then ![]() .
.
The upshot of this lemma is: A function ![]() in
in ![]() that is not of the form
that is not of the form ![]() for some function
for some function ![]() must necessarily have Birkhoff sums that are unbounded from below and, indeed, also from above, as can be seen by passing to
must necessarily have Birkhoff sums that are unbounded from below and, indeed, also from above, as can be seen by passing to ![]() . In other words, the Birkhoff sums of a usual function in
. In other words, the Birkhoff sums of a usual function in ![]() will exhibit strong oscillating behavior. To be fair, one has to admit that this lemma is not quite what one would hope for since it is not clear (to me) whether h is integrable and hence
will exhibit strong oscillating behavior. To be fair, one has to admit that this lemma is not quite what one would hope for since it is not clear (to me) whether h is integrable and hence ![]() . However, for establishing oscillating behavior, it is sufficient to represent
. However, for establishing oscillating behavior, it is sufficient to represent ![]() as
as ![]() , regardless of whether
, regardless of whether ![]() is integrable or not. Thus, our quest remains unaffected!
is integrable or not. Thus, our quest remains unaffected!
Proof. For almost every ![]() ,
,
![]()
Therefore, the set ![]() is
is ![]() -invariant and so
-invariant and so ![]() by ergodicity. If
by ergodicity. If ![]() , we already know by definition that
, we already know by definition that ![]() and so
and so ![]() , showing that
, showing that ![]() is finite almost everywhere. In this case, we can rearrange the above inequality to
is finite almost everywhere. In this case, we can rearrange the above inequality to ![]() .
.
To see that equality holds, note that ![]() , so this function has a well-defined (possibly infinite) integral. (We do not know whether
, so this function has a well-defined (possibly infinite) integral. (We do not know whether ![]() is integrable.) Therefore, by a slight generalization of Birkhoff’s ergodic theorem using cutt-offs,
is integrable.) Therefore, by a slight generalization of Birkhoff’s ergodic theorem using cutt-offs,
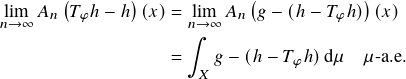
since ![]() . If we can show that this vanishes, then
. If we can show that this vanishes, then ![]() since a positive function with zero integral vanishes. However, for almost every
since a positive function with zero integral vanishes. However, for almost every ![]()
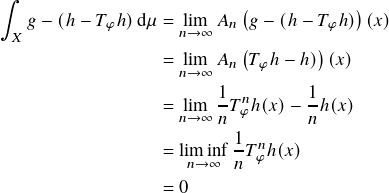
since by Poincaré recurrence, almost every ![]() returns infinitely often to a set
returns infinitely often to a set
of positive measure where ![]() is bounded. Hence,
is bounded. Hence, ![]() .
. ![]()
With this criterion in our pocket, Atkinson’s lemma is a piece of cake.
Proof (of Atkinson’s Lemma). First, suppose ![]() can be written as
can be written as
![]()
for some (not necessarily integrable) ![]() . Then the claim is immediate if
. Then the claim is immediate if ![]() is essentially constant and follows swiftly from Poincaré recurrence otherwise since
is essentially constant and follows swiftly from Poincaré recurrence otherwise since ![]() will oscillate almost everywhere. If
will oscillate almost everywhere. If ![]() does not admit such a representation, then neither does
does not admit such a representation, then neither does ![]() and so by the lemma above the Birkhoff sums
and so by the lemma above the Birkhoff sums ![]() must be unbounded from above and below, i.e.,
must be unbounded from above and below, i.e.,
![]()
In particular, for almost every ![]()
![]()
each hold infinitely often. Dividing by ![]() yields the claim.
yields the claim. ![]()
The lemma that we used should be compared to the Gottschalk-Hedlund Theorem in topological dynamics:
Theorem. Let ![]() be a minimal topological dynamical system on a compact metric space
be a minimal topological dynamical system on a compact metric space ![]() . If
. If ![]() , then
, then